HyPhy v2.3 Quick Start#
CAUTION: This tutorial is for the development branch of HyPhy only! This tutorial is not compatible with the current release. Please see this tutorial for information on using the current HyPhy release.
This tutorial outlines how to prepare data and execute analyses for use in the following methods:
Note that you can additional use these methods via the development version of Datamonkey (RELAX and BUSTED) or the current version of Datamonkey (FEL).
If you do not have a dataset to work with, you might find it convenient to download this zip file with some example datasets.
Installation#
CAUTION : This is for the development branch of HyPhy only!
Dependencies#
Commands#
Build the development branch of HyPhy on your system by issuing the following commands.
git clone https://github.com/veg/hyphy.git cd hyphy git checkout v2.3-dev cmake . # Requires version > 3.0 make MP # openMP should be installed in your system for optimal performance # For faster make, try "make -j MP".
Do not run make install as you will encounter conflicts with any other HyPhy versions installed in your system.
Check that the HyPhy build was successful using the following command issued from the hyphy/ directory:
./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res ./tests/hbltests/libv3/math.bf
If HyPhy is working correctly, you should see the following output:
{
"Count":4,
"Mean":2.25,
"Median":2,
"Min":1,
"Max":4,
"2.5%":1,
"97.5%":4,
"Sum":9,
"Std.Dev":1.089724735885168,
"Variance":1.1875,
"COV":0.4843221048378527,
"Skewness":0.6520236646847543,
"Kurtosis":2.096952908587258,
"Sq. sum":18,
"Non-negative":4
}
Note that all examples below will assume that a tree has not been defined within your dataset (e.g. FASTA or NEXUS) file. If you opt to use a data file that contains a tree, some of the prompts may change. Specifically, you will not need to provide HyPhy with a separate file containing a tree, but you will have to confirm that HyPhy should use the provided tree.
Use RELAX to compare selective pressures on different parts of the tree#
RELAX is a method described in Wertheim et al. It is based on the BS-REL model branch site framework, but the tree is partitioned (a priori) into non-overlapping sets of branches. Separate distributions of are fitted to each set and compared for relative relaxation ( values contract to 1) or intensification ( values move away from 1) of selection pressure.
Note that you can use RELAX via Datamonkey, you can or follow this tutorial to use RELAX in the current version of HyPhy. Otherwise, follow these directions to run RELAX in the development branch of HyPhy:
-
To use RELAX, you must first prepare your data by partitioning branches into two sets of non-overlapping branches: The reference branch set and the test branch set. The RELAX test for relaxation/intensification of selection pressure will be run on the test branches relative to the baseline reference branches. The easiest way to partition your newick tree is using the web-based phylotree application, as demonstrated:
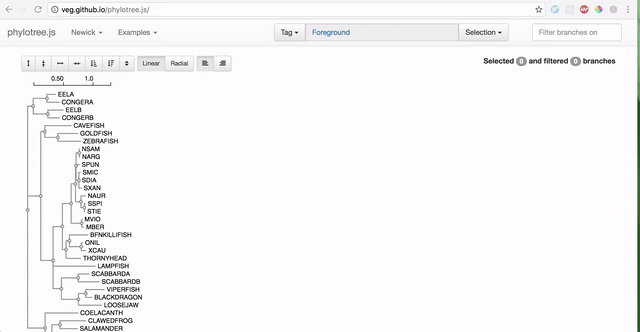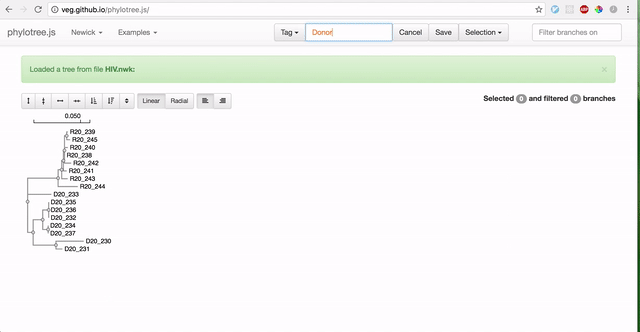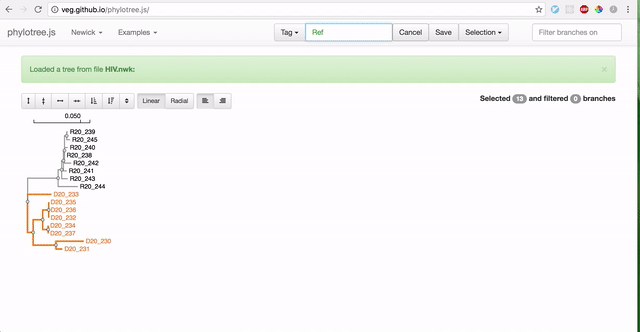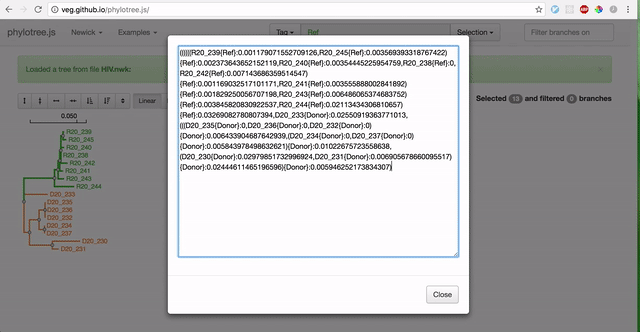
-
Launch a terminal session and navigate to the directory where you have compiled the development version of HyPhy. From within this directory, issue the following command to run RELAX and respond to the prompts. Be sure to provide absolute paths for all file names prompted.
./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/RELAX.bf
-
Alternatively, you can pipe the arguments directly into the HyPhy call to RELAX.
./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/RELAX.bf
-
In the above example, the piped arguments correspond to the following:
1- Select the Universal Code<path to sequence file>- the absolute path/filename of the multiple sequence alignment<path to tree file>- the absolute path/filename of the labeled newick tree3- Selects tagged partition for testing relaxed selection2- Selects tagged partition for reference branches1- Fits descriptive models and run the relax test (4 models) as opposed to a minimal RELAX test (2 models)
-
-
Once the RELAX job is completed, there will be a file that is generated in the same directory as the sequence file named
<sequence-file>.RELAX.json. The file is standard JSON, and can be parsed with any programming language. You can also visualize, explore, and obtain plots from this JSON file using the HyPhy Vision web application.
Use BUSTED to test for alignment-wide episodic diversification#
BUSTED is a method described in Murrell et al. It has been extensively tested and shows better power and accuracy than either "branch-site" models in PAML, or the "covarion" style models.
Note that you can use BUSTED via Datamonkey, you can or follow this tutorial to use BUSTED in the current version of HyPhy. Otherwise, follow these directions to run BUSTED in the development branch of HyPhy:
-
If you would like to use BUSTED to test specific foreground branches for episodic selection, you must prepare your newick phylogeny with annotated branches. To accomplish this, we recommend using the web-based phylotree widget, as demonstrated below. Export and save this annotated tree for use in BUSTED. Alternatively, you can analyze the entire tree for episodic diversification, in which case branch annotation is not needed and a "regular" newick tree will be fine.
-
Launch a terminal session and navigate to the directory where you have compiled the development version of HyPhy. From within this directory, issue the following command to run BUSTED and respond to the prompts. Be sure to provide absolute paths for all file names prompted.
./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/BUSTED.bf
-
Alternatively, you can pipe the arguments directly into the HyPhy call to BUSTED. Note that, as written, this command will instruct BUSTED to consider all branches as foreground:
(echo 1; echo <path to sequence file>; echo <path to tree file>; echo 4; echo d) | ./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/RELAX.bf
-
In the above example, the piped arguments correspond to the following:
1- Select the Universal Code<path to sequence file>- the absolute path/filename of the multiple sequence alignment<path to tree file>- the absolute path/filename of the labeled newick tree4- Test for selection on all branches labeled with {FOREGROUND} jointlyd- Complete branch selection
-
Once the BUSTED job is completed, there will be a file that is generated in the
same directory as the sequence file named <sequence-file>.BUSTED.json. The file is standard JSON, and can be parsed with any programming language. You can also visualize, explore, and obtain plots from this JSON file using the HyPhy Vision web application.
FEL - Fixed Effects Model for detecting site-wise selective pressure#
FEL is described in Pond and Frost. FEL estimates site-wise synonymous () and non-synonymous () rates, and uses a likelihood ratio test to determine if at each site. The estimates aggregate information over all branches, so the signal is derived from pervasive diversification or conservation.
Note that you can use FEL via Datamonkey, you can or follow this tutorial to use FEL in the current version of HyPhy. Otherwise, follow these directions to run FEL in the development branch of HyPhy:
Please also note that FEL is an MPI-aware script. You are free to use HYPHYMPI (instead of HYPHYMP) in conjunction with mpirun on computing clusters for improved performance.
-
Launch a terminal session and navigate to the directory where you have compiled the development version of HyPhy. From within this directory, issue the following command to run BUSTED and respond to the prompts. Be sure to provide absolute paths for all file names prompted.
./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/FEL.bf
-
Alternatively, you can pipe the arguments directly into the HyPhy call to BUSTED. Note that, as written, this command will instruct BUSTED to consider all branches as foreground:
(echo 1; echo <path to sequence file>; echo <path to tree file>; echo 1; echo 0.1) | ./HYPHYMP LIBPATH=`pwd`/res res/TemplateBatchFiles/SelectionAnalyses/FEL.bf
-
In the above example, the piped arguments correspond to the following:
1- Select the Universal Code<path to sequence file>- the absolute path/filename of the multiple sequence alignment<path to tree file>- the absolute path/filename of the labeled newick tree1- Include all branches in the analysis0.1- Significance (p-value) threshold for identifying selected sites
-
-
FEL will now run to completion. While running, it will print out a table of site-specific inferences specifically for those sounds found to be under selection (either negative or positive):
| Codon | Partition | alpha | beta | LRT |Selection detected?| |:--------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:-----------------:| | 12 | 1 | 10.917 | 0.000 | 2.931 | Neg. p = 0.0869 | | 18 | 1 | 54.146 | 0.000 | 8.159 | Neg. p = 0.0043 | | 20 | 1 | 25.068 | 0.000 | 2.827 | Neg. p = 0.0927 | | 88 | 1 | 37.678 | 0.000 | 4.004 | Neg. p = 0.0454 | | 93 | 1 | 26.041 | 0.000 | 3.142 | Neg. p = 0.0763 | | 101 | 1 | 9.866 | 0.000 | 2.894 | Neg. p = 0.0889 | | 134 | 1 | 25.423 | 0.000 | 3.949 | Neg. p = 0.0469 | | 159 | 1 | 23.622 | 0.000 | 3.895 | Neg. p = 0.0484 |
These columns are as follows:
Codon: The codon site.Partition: The partition for this codon. If the analysis was not partitioned, all codons are in partition 1.alpha: The estimated dS parameter at this site.beta: The estimated dN parameter at this site.LRT: The likelihood ratio test statistic for comparing null and alternative models to test for selection.Selection Detected?: Indicates whether this site shows evidence for negative (Neg.) or positive (Pos.) selection and the associated p-value.
Once the FEL job is completed, there will be a file that is generated in the
same directory as the sequence file named <sequence-file>.fel.json. The file is standard JSON, and can be parsed with any programming language. Currently it is not possible to explore this JSON with HyPhy Vision although this functionality is expected soon.